Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Takata, Takashi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Tsuda, Shuichi; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 198(17), p.1283 - 1291, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Spherical or cylindrical detectors superior to directional characteristic are commonly used to monitor dose rates in the environment to detect scattering gamma-rays emitted from radionuclides in soil or air. The authors have performed environmental dose rates measurements using various kinds of detectors to investigate the directional characteristics, and experimentally verified the variations in dose rates due to directional characteristics unique to each detector. Furthermore, a dose rate measured by a CsI(Tl) scintillation detector with cuboidal crystal agreed with that by a CsI(Tl) scintillation detector with cylindrical crystal. Simulations by PHITS under various CsI(Tl) crystal configurations revealed that there are certain aspect ratios of cuboidal CsI(Tl) crystal with less directional dependence. Since cubes are advantageous in terms of production cost, this result indicates the potential of CsI(Tl) scintillation detectors with cuboidal crystal for use in the environmental dose rate monitoring.
 *(10) dose rates measured in environment contaminated by radioactive caesium; Correction of directional dependence of scintillation detectors
*(10) dose rates measured in environment contaminated by radioactive caesium; Correction of directional dependence of scintillation detectorsTsuda, Shuichi; Tanigaki, Minoru*; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Okumura, Ryo*; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 193(3-4), p.228 - 236, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.78(Environmental Sciences)Environmental dose rate monitoring has been performed with various scintillation detectors since the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Gamma-rays from caesium isotopes deposited in soil enter radiation detectors in any direction, but directional dependence of the detectors used for dose rate measurements are not always uniform and the dose rates vary even if measurement takes place at the same place. To investigate the influence of crystal configurations on dose rate, dose rate measurements using several scintillation detectors with different crystal configurations were conducted. By measuring pulse height spectra and multiplying them with spectrum - dose conversion operators (G(E) function), dose rates were deduced and compared. It was found that the dose rates varied within approximately 25% among six detectors. To reduce the differences, the dose rate using G(E) functions determined in rotational geometry were obtained and applied instead. The revised dose rates agreed with one another within uncertainties, but this was not the case of scintillation detector with flat crystal shape, and it means this method could not compensate its strong directional dependence. These experimental results reveal that detectors with superior directional characteristics should be used for environmental dose rate measurement since the compensation of directional dependence using a G(E) function determined in rotational geometry is not always available.
Miyahara, Shinya*; Ohdaira, Naoya*; Arita, Yuji*; Maekawa, Fujio; Matsuda, Hiroki; Sasa, Toshinobu; Meigo, Shinichiro
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 352, p.110192_1 - 110192_8, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Lead-Bismuth Eutectic (LBE) is used as a spallation neutron target and coolant materials of Accelerator Driven System (ADS), and many kinds of elements are produced as spallation products. It is important to evaluate the release and transport behavior of the spallation products in the LBE. The inventories and the physicochemical composition of the spallation products produced in LBE have been investigated for an LBE loop in the ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) in J-PARC. The inventories of the spallation products in the LBE were estimated using the PHITS code. The physicochemical composition of the spallation products in the LBE was calculated using the Thermo-Calc code under the conditions of the operation temperatures of LBE from 350 C to 500
C to 500 C and the oxygen concentrations in LBE from 10 ppb to 1 ppm. The calculation showed that the 5 elements of Rb, Tl, Tc, Os, Ir, Pt, Au and Hg were soluble in LBE under the all given conditions and any kinds of compound were not formed in LBE. It was suggested that the oxides of Ce, Sr, Zr and Y were stable as CeO
C and the oxygen concentrations in LBE from 10 ppb to 1 ppm. The calculation showed that the 5 elements of Rb, Tl, Tc, Os, Ir, Pt, Au and Hg were soluble in LBE under the all given conditions and any kinds of compound were not formed in LBE. It was suggested that the oxides of Ce, Sr, Zr and Y were stable as CeO , SrO, ZrO
, SrO, ZrO and Y
and Y O
O in the LBE.
in the LBE.
Hanada, Masaya; Seki, Takayoshi*; Takado, Naoyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Sakamoto, Keishi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Fusion, 46(6), p.S318 - S323, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:69.47(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The origin of the beam non-uniformity, that is one of the key issues in large Cs-seeded negative ion sources for JT-60U and ITER, was experimentally examined by measuring correlations between the intensity of the H ion beam and plasma parameters such as an electron temperature and plasma density in the JAERI 10 A negative ion source. From the correlation between the beam intensity and the plasma parameters, it was foreseen that the beam non-uniformity was due to the localization of the plasma and/or H0 atoms caused by B x
ion beam and plasma parameters such as an electron temperature and plasma density in the JAERI 10 A negative ion source. From the correlation between the beam intensity and the plasma parameters, it was foreseen that the beam non-uniformity was due to the localization of the plasma and/or H0 atoms caused by B x 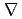 B drift of the fast electron from filaments. The filament position was modified to suppress the B x
B drift of the fast electron from filaments. The filament position was modified to suppress the B x 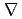 B drift, and then the spatial uniformity of the beam intensity was examined. By this modification, the root-mean-square deviation of the spatial beam intensity from the averaged value deceased to a half of that before modification while the beam intensity integrated along the longitudinal direction was kept to be constant. From this result, it was confirmed that one of the origin of the beam non-uniformity was caused by plasma localization.
B drift, and then the spatial uniformity of the beam intensity was examined. By this modification, the root-mean-square deviation of the spatial beam intensity from the averaged value deceased to a half of that before modification while the beam intensity integrated along the longitudinal direction was kept to be constant. From this result, it was confirmed that one of the origin of the beam non-uniformity was caused by plasma localization.
Galatanu, A.; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Ikeda, Shugo; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Aoki, Dai*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Onuki, Yoshichika
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 74(5), p.1582 - 1597, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:80.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the magnetic property of typical uranium compounds by measuring the magnetic susceptibility in an extended temperature range up to about 800 K. The magnetic susceptibility follows the Curie-Weiss law for a localized 5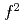 -electron compound UPd
-electron compound UPd and a ferromagnetic insulator UFe
and a ferromagnetic insulator UFe P
P . In most of the investigated compounds we observed a crossover effect of the 5
. In most of the investigated compounds we observed a crossover effect of the 5 electrons from a low-temperature itinerant nature to a high-temperature localized one. This is found to be characteristic for ferromagnetic superconductors such as UGe
electrons from a low-temperature itinerant nature to a high-temperature localized one. This is found to be characteristic for ferromagnetic superconductors such as UGe and UIr, and also for antiferromagnets like USb
and UIr, and also for antiferromagnets like USb or UNiSb
or UNiSb . To assess an extension of this characteristic property in the uranium compounds we also investigated typical 5
. To assess an extension of this characteristic property in the uranium compounds we also investigated typical 5 -itinerant compounds like UGa
-itinerant compounds like UGa and UPtGa
and UPtGa . The crossover effect is essentially important in heavy fermion compounds such as UPt
. The crossover effect is essentially important in heavy fermion compounds such as UPt , UPd
, UPd Al
Al and URu
and URu Si
Si . Even in the paramagnetic compound of UB
. Even in the paramagnetic compound of UB , the magnetic susceptibility is not temperature-independent, but approaches a 5
, the magnetic susceptibility is not temperature-independent, but approaches a 5 -localized tendency at high temperatures. Since the samples were single crystals, we were also able to trace the evolution of the magnetic anisotropy. The high-temperature anisotropic susceptibility data were analyzed on the basis of the crystalline electric field scheme.
-localized tendency at high temperatures. Since the samples were single crystals, we were also able to trace the evolution of the magnetic anisotropy. The high-temperature anisotropic susceptibility data were analyzed on the basis of the crystalline electric field scheme.
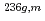 Am and its EC-decay daughter
Am and its EC-decay daughter  Pu
PuAsai, Masato; Sakama, Minoru*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Goto, Shinichi*; Kojima, Yasuaki*; Oura, Yasuji*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 23(3), p.395 - 400, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:71.27(Physics, Nuclear)The EC decay of  Am has been studied through
Am has been studied through  -ray spectroscopy. Two EC-decaying states have been found in
-ray spectroscopy. Two EC-decaying states have been found in  Am with half-lives of 3.6 min and 2.9 min. In
Am with half-lives of 3.6 min and 2.9 min. In  Pu, we have found the
Pu, we have found the 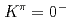 octupole band and two-quasiparticle states one of which is a
octupole band and two-quasiparticle states one of which is a  isomer with a 1.2
isomer with a 1.2  s half-life. The EC transitions from
s half-life. The EC transitions from 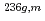 Am to the two-quasiparticle states in
Am to the two-quasiparticle states in  Pu show small
Pu show small 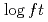 values of 4.8--5.3, which allowed us to assign proton-neutron configurations of
values of 4.8--5.3, which allowed us to assign proton-neutron configurations of 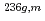 Am and the two-quasiparticle states.
Am and the two-quasiparticle states.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Akimoto, Hajime
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2003-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu, Vol.3, p.247 - 248, 2003/08
We start R&D project to develop the predictable technology for thermal-hydraulic performance of Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) in collaboration with power company/reactor vendor/university since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured BWR technologies. MOX fuel assemblies with tight lattice arrangement are used to increase the conversion ratio by reducing the moderation of neutron energy. Increasing the in-core void fraction also contributes to the reduction of neutron moderation. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight lattice configuration. This series presentation focuses on the feasibility study and shows the R&D plan using large-scale test facility and advanced numerical simulation technology.
Takase, Kazuyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Advanced Fluid Information (AFI-2001), p.227 - 232, 2001/10
no abstracts in English
Iwai, Yasunori; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Nishi, Masataka
JAERI-Tech 2001-027, 29 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Tabata, Yoneho*; Oshima, Akihiro
Macromolecular Symposia, 143, p.337 - 358, 1999/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:76.14(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
*; *; *; Seguchi, Tadao; Tabata, Yoneho*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 55(4), p.399 - 408, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:72.26(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 A' electronic states of H
A' electronic states of H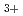
Ichihara, Akira; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Iwamoto, Osamu
JAERI-Data/Code 98-031, 18 Pages, 1998/11
no abstracts in English
T.V.Hung*; Sakamoto, Yukio; Yasuda, Hideshi
JAERI-Research 98-057, 25 Pages, 1998/10
no abstracts in English
Tokuda, Shinji; *
JAERI-Research 97-034, 53 Pages, 1997/05
no abstracts in English
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 32(9), p.889 - 897, 1995/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
JAERI-Data/Code 95-001, 62 Pages, 1995/03
no abstracts in English
Horiike, Hiroshi; Ando, Toshiro; ; *; Koizumi, Koichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Shimizu, Masatsugu; Yamamoto, Masahiro
1989 IEEE 13th Symp. on Fusion Engineering,Vol. 2, p.1049 - 1054, 1990/00
no abstracts in English
Takamura, Saburo; ; *; *
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 1, p.4519 - 4526, 1989/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.73(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 86-177, 44 Pages, 1986/12
no abstracts in English